GRAB at the Crossroads!
Scale, Profitability, and the Long Road from Super-App to Cash Machine
Executive Summary
GRAB operates Southeast Asia’s leading superapp platform across deliveries, mobility, and financial services. Revenue model centers on transaction-based fees and commissions from driver-partners, merchant-partners, and consumers across 800+ cities in eight countries. The company generates revenue through three segments: Deliveries (food and grocery delivery), Mobility (ride-hailing), and Financial Services (digital payments, lending, digital banking).
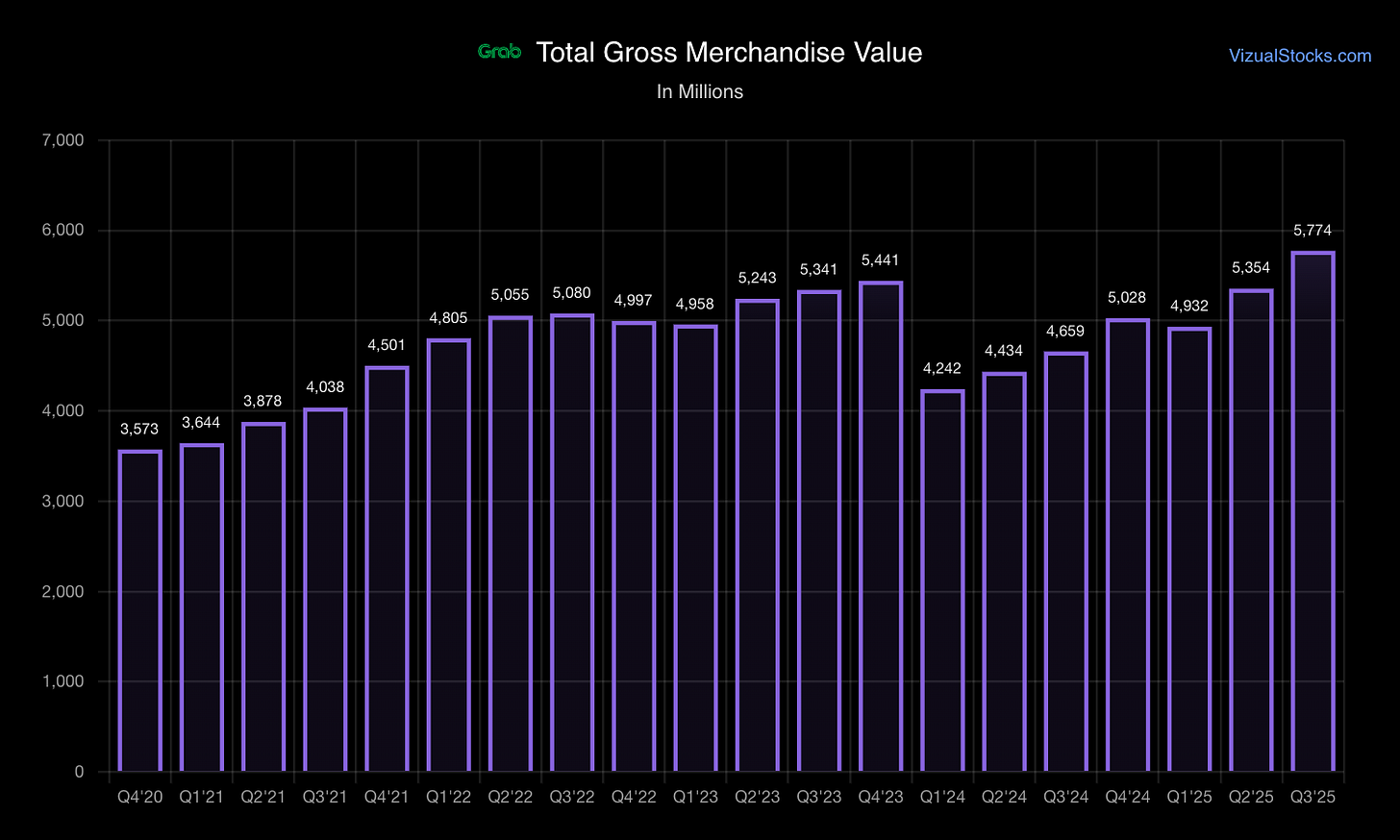
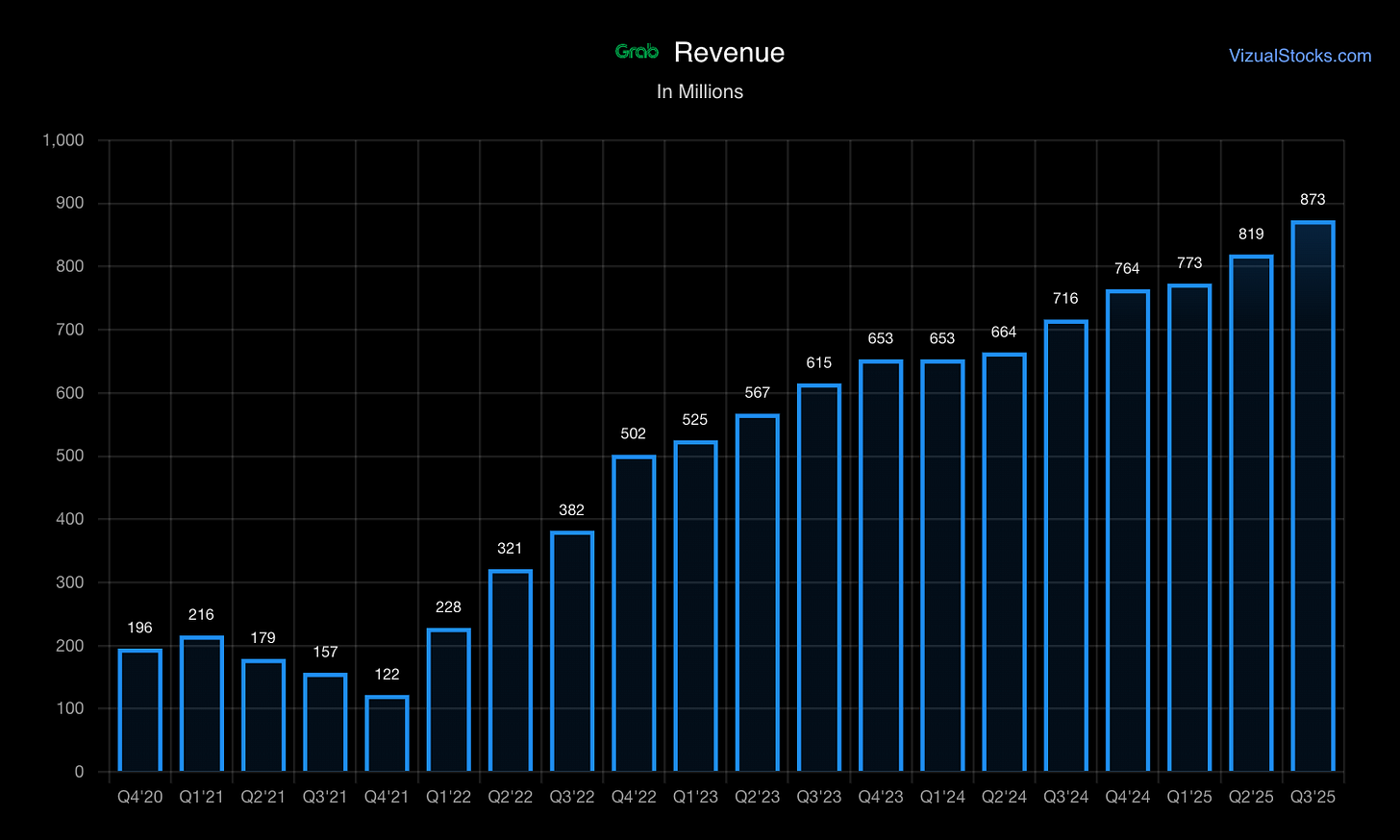
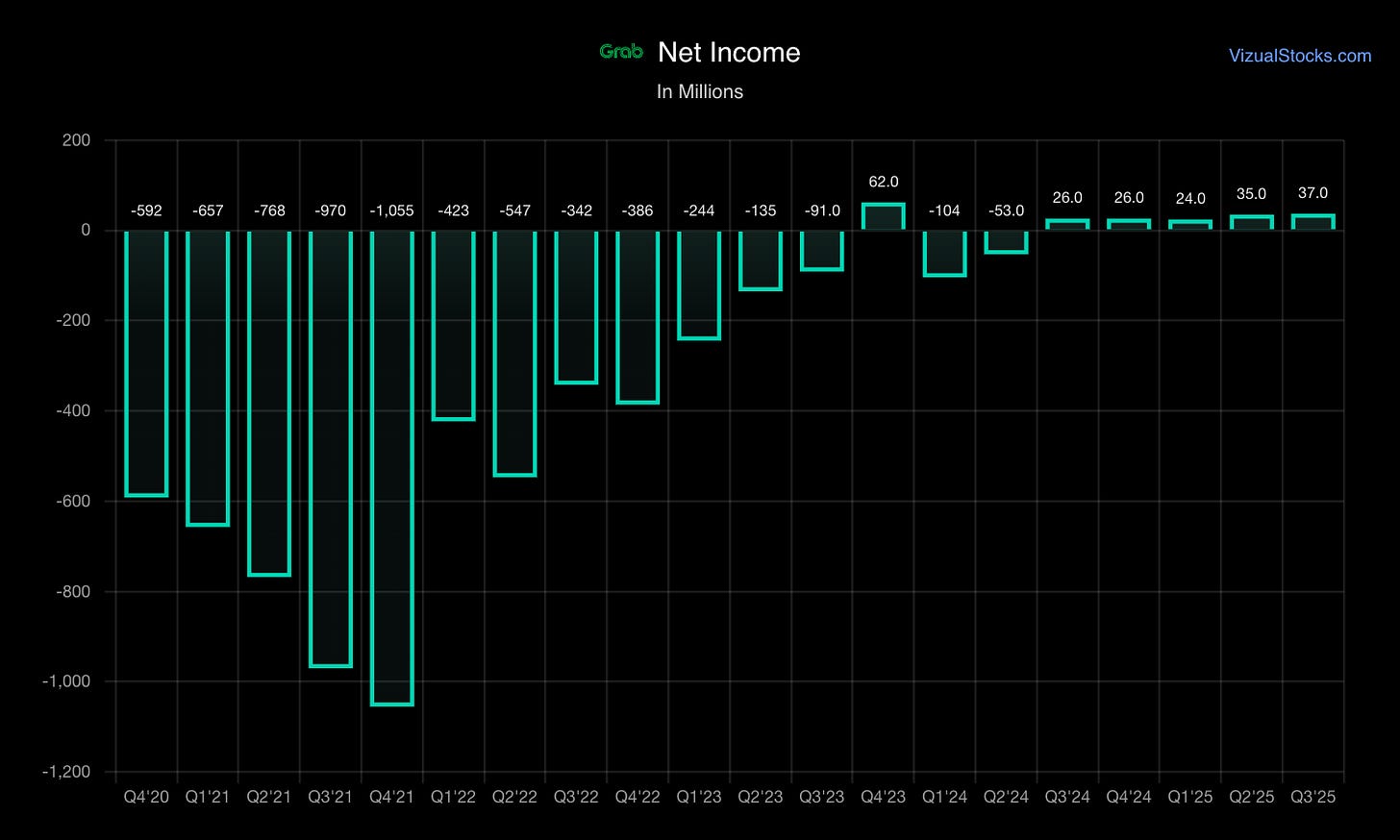
Business Quality: The economics show improving trajectory—GRAB achieved GAAP profitability in Q4 2023 (EPS $0.01) and has maintained positive quarterly earnings through 2024-2025. Revenue grew 21-23% YoY in recent quarters ($873M in Q3’25), with gross margins improving as incentive spending stabilizes at ~10% of GMV. However, the business remains capital-intensive with ongoing investments in digital banking, autonomous vehicles, and regional expansion.
Key Risks: Intense regional competition [Gojek (atleast on paper), Foodpanda, ShopeeFood], regulatory uncertainty across eight jurisdictions, driver classification battles, and execution risk in new ventures (digital banking, AV technology). The company faces potential reclassification of driver-partners as employees, variable regulatory frameworks, and dependence on incentive spending to maintain market position.
In Plain English: GRAB is the “Amazon meets Uber” of Southeast Asia—a superapp where you order food, hail rides, send packages, make payments, and now even get loans, all while navigating one of the world’s most complex regulatory environments.
Source: Fiscal.ai
What They Sell and Who Buys
Core Offerings:
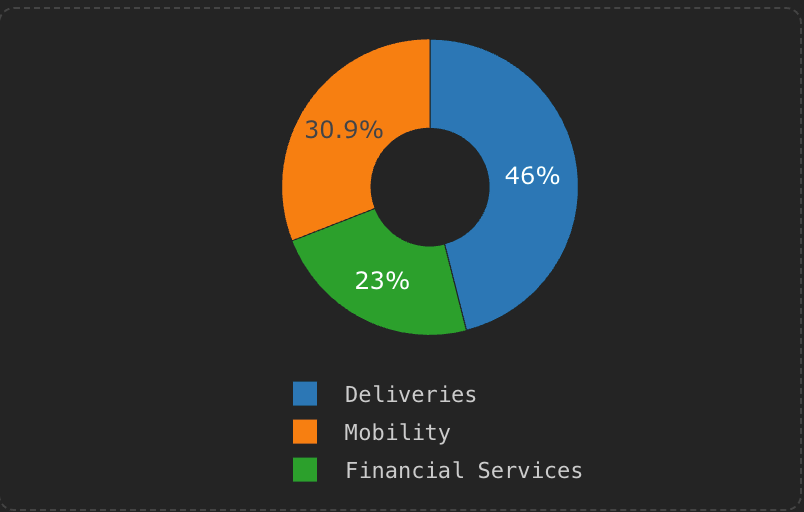
Deliveries (46% of GMV): Food delivery, grocery, package/parcel delivery, instant commerce
Mobility (31% of GMV): Ride-hailing (4-wheel, 2-wheel, 3-wheel), car rentals, emerging AV services
Financial Services (23% of GMV): GrabPay wallet, digital banking (Singapore, Malaysia, Indonesia), lending, insurance distribution, payments processing
Customer Segments:
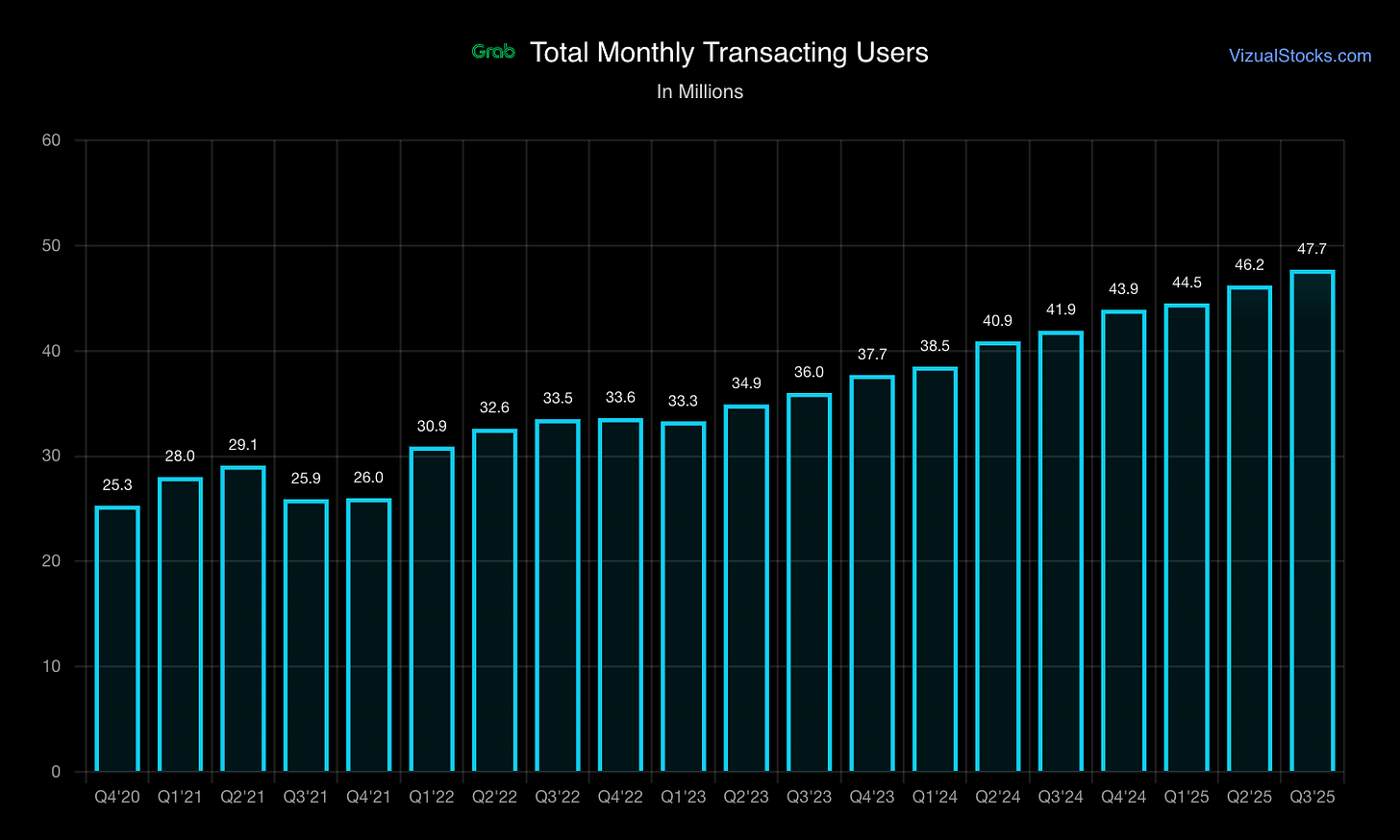
Consumers: 41.3M monthly transacting users (MTUs) as of FY2024, primarily middle-income urban residents across Singapore, Malaysia, Indonesia, Thailand, Vietnam, Philippines, Cambodia, Myanmar
Driver-Partners: Hundreds of thousands providing mobility and delivery services
Merchant-Partners: Restaurants, retailers, grocers, convenience stores seeking access to digital consumer base
Purchase Motivation: Convenience, price competitiveness, integrated ecosystem benefits (pay for rides with GrabPay, earn rewards across services), trust in established brand, superior technology platform versus fragmented alternatives.
How They Make Money
Revenue Model: Predominantly transaction-based with increasing recurring elements
Commission-Based (Primary): GRAB takes 15-30% commissions from completed transactions—ride fares, delivery orders, merchant sales
Service Fees: Direct charges to consumers (delivery fees, booking fees, surge pricing)
Financial Services Revenue: Transaction fees, lending interest, insurance commissions, payment processing fees
Advertising: Merchant advertising within the app
Revenue Composition (Q3’25: $873M):
Chart: Revenue Mix by Segment (Q3’25)Estimated segment revenue breakdown
Revenue reported NET of partner/consumer incentives — Incentives totaled $1.8B in FY2024, reducing reported revenue by the same amount.
Revenue Quality
Predictability: Moderate to High
Transaction-based model creates inherent variability but high frequency (millions daily) smooths volatility
41.3M MTUs provide large, stable base with low individual customer concentration
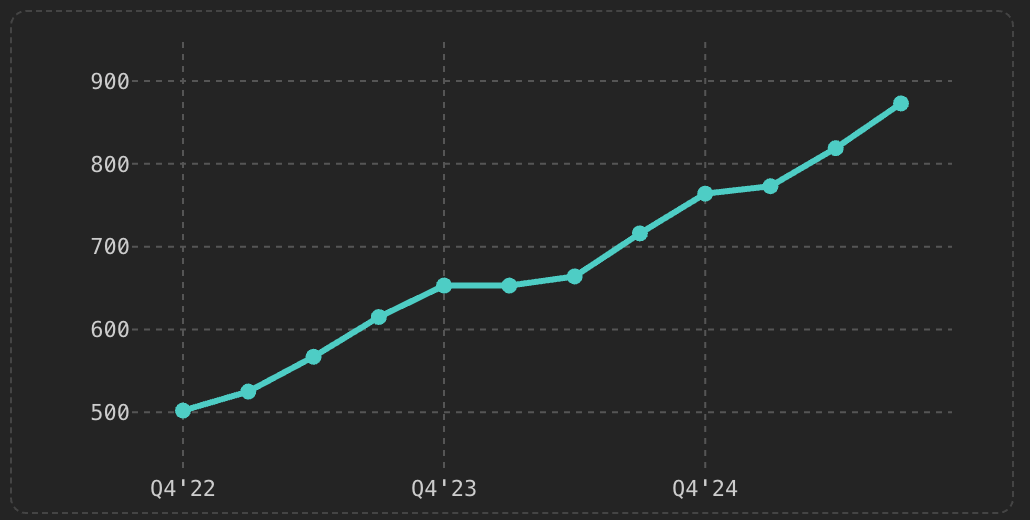
Sequential quarterly growth remarkably consistent: 16-24% YoY across last 8 quarters
Recurring vs. One-Time Exposure:
High Recurring (85%+): Daily needs (food, transportation) drive repeat usage; average user transacts 25-30x annually
Emerging Recurring (Financial Services): Loan products, insurance, digital banking deposits create longer-term revenue streams
Low One-Time Exposure: Minimal project-based or large one-off transactions
Concentration Risks:
Chart: Quarterly Revenue TrajectorySource: Company earnings releases, Q4’22-Q3’25
Quality Assessment: Revenue predictability improving as ecosystem matures. Incentive discipline (stabilized at 10% of GMV) demonstrates pricing power. Geographic concentration and regulatory exposure remain material concerns.
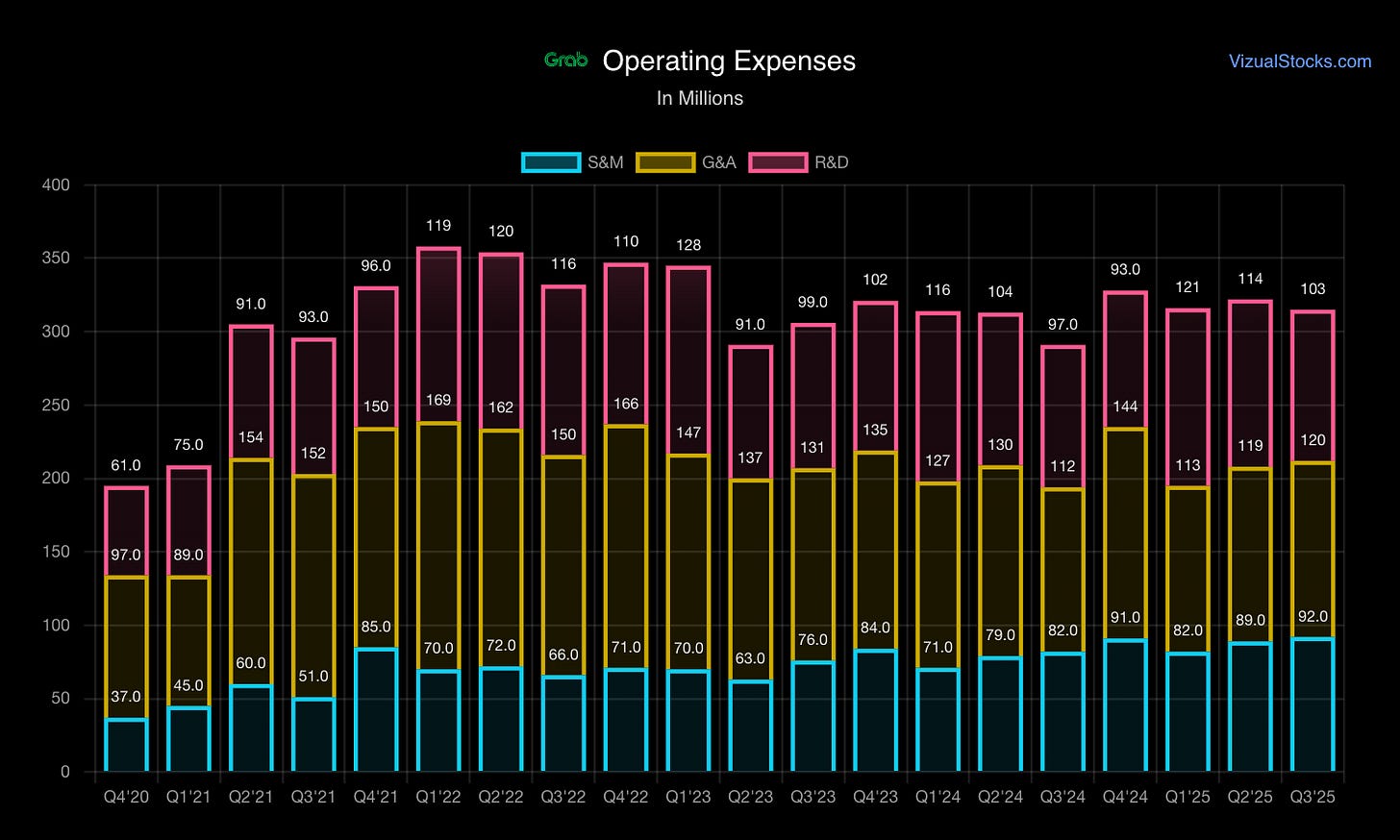
Cost Structure
Major Cost Components:
Partner & Consumer Incentives (Largest Variable Cost): $1.8B in FY2024
Driver incentives to maintain supply
Consumer promotions for demand generation
Merchant subsidies for platform attractiveness
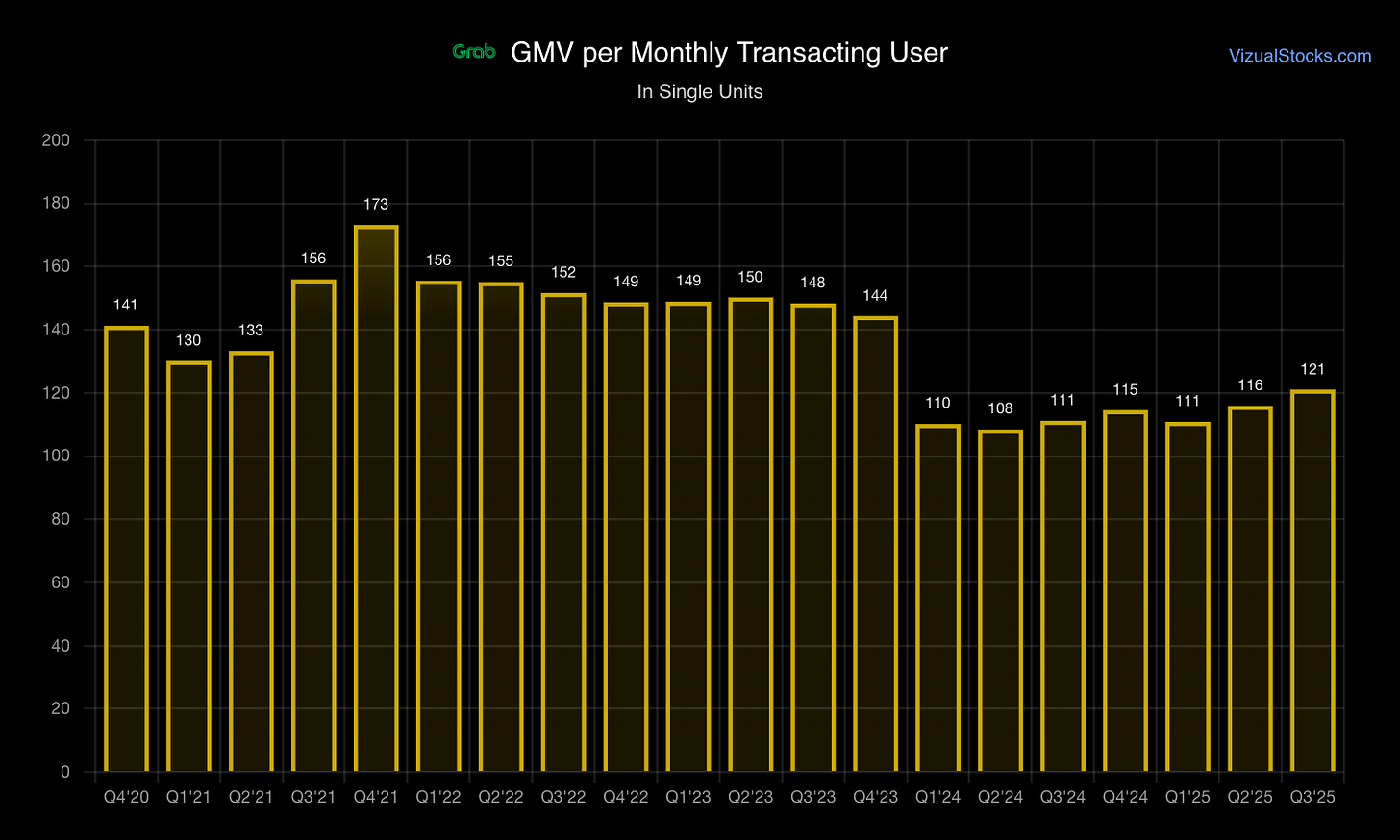
Key Metric: On-demand incentives = 10% of GMV (stable vs. 13.3% in 2022)
Cost of Revenue: Payment processing fees, hosting infrastructure, delivery partner costs (under principal model in select markets)
Sales & Marketing: Regional advertising, user acquisition, brand building across 8 countries
Technology & Development: Engineering talent (scarce/expensive in SEA), platform maintenance, new product development (AV, digital banking, GrabMaps)
General & Administrative: Regional HQ operations, compliance, legal (8 regulatory jurisdictions)
Margin Profile:
Metric | Current Estimate | Trend
Gross Margin | 40-45% | ↑ Improving
Operating Margin | 5-8% | ↑ Recently positive
Net Margin | ~0-2% | ↑ Just achieved profitability
Scalability: High incremental margins once liquidity established in a market (network effects). However, new market/product launches reset investment cycle. Digital banking particularly capital-intensive in early stages.
Capital Intensity
Asset Requirements:
Light Asset Model (Core Business): Drivers/merchants own vehicles/inventory; GRAB provides platform
Heavy Investment (Growth Initiatives):
Digital banking: Regulatory capital requirements, loan loss reserves, infrastructure
Autonomous vehicles: $60M investment in Vay (remote driving), partnerships with WeRide and May Mobility
Technology infrastructure: Cloud hosting, data centers, proprietary mapping (GrabMaps)
M&A: Infermove acquisition (AI robotics, Jan 2026)
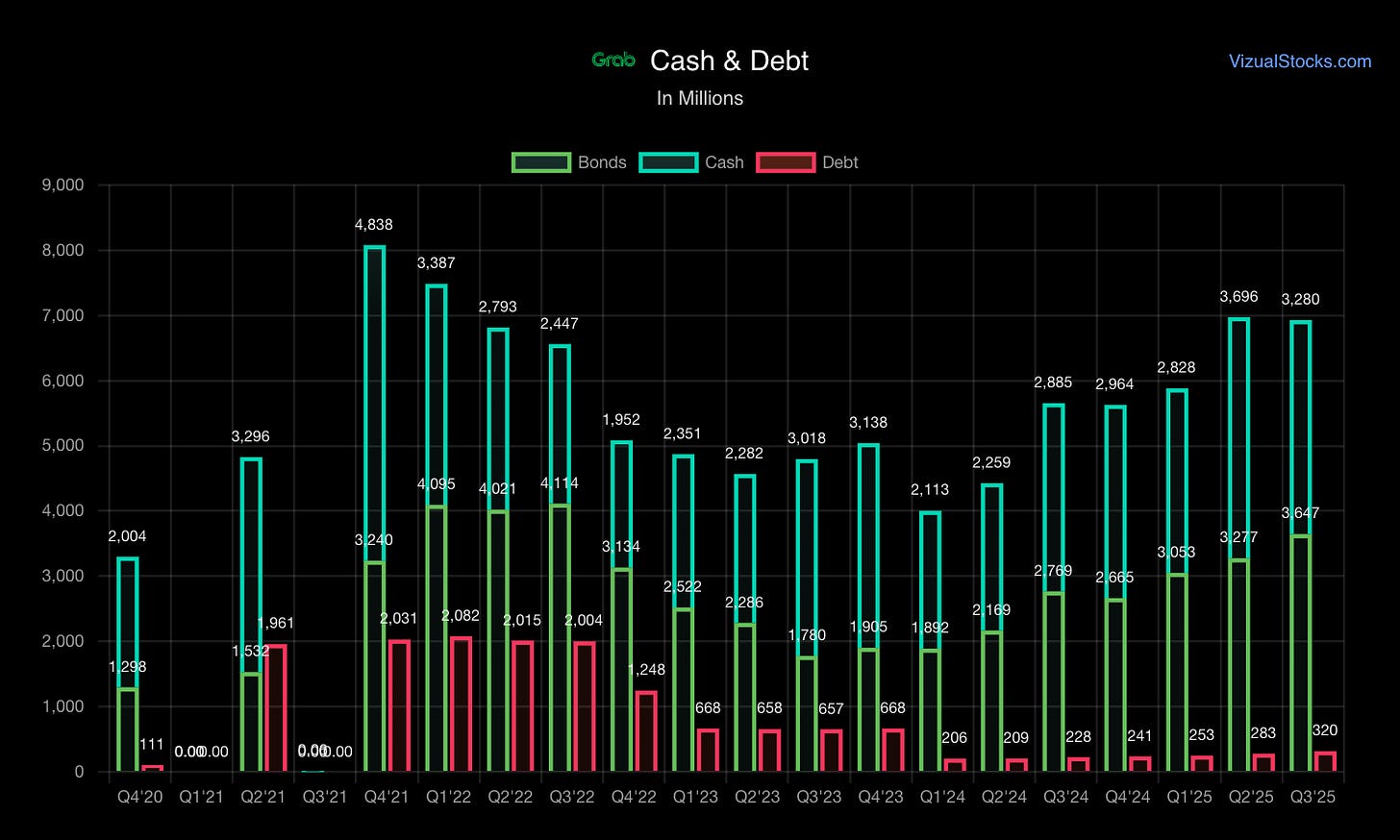
Financial Position (as of Q3 2025 Earnings):
Cash, deposits, debt investments: ~$6.9B
Total assets: ~$11.4B
Access to capital markets via NASDAQ listing
Capex Trends: Increasing as digital banking scales and AV investments accelerate. Digital banks in Singapore/Malaysia/Indonesia require ongoing capital injections pre-profitability.
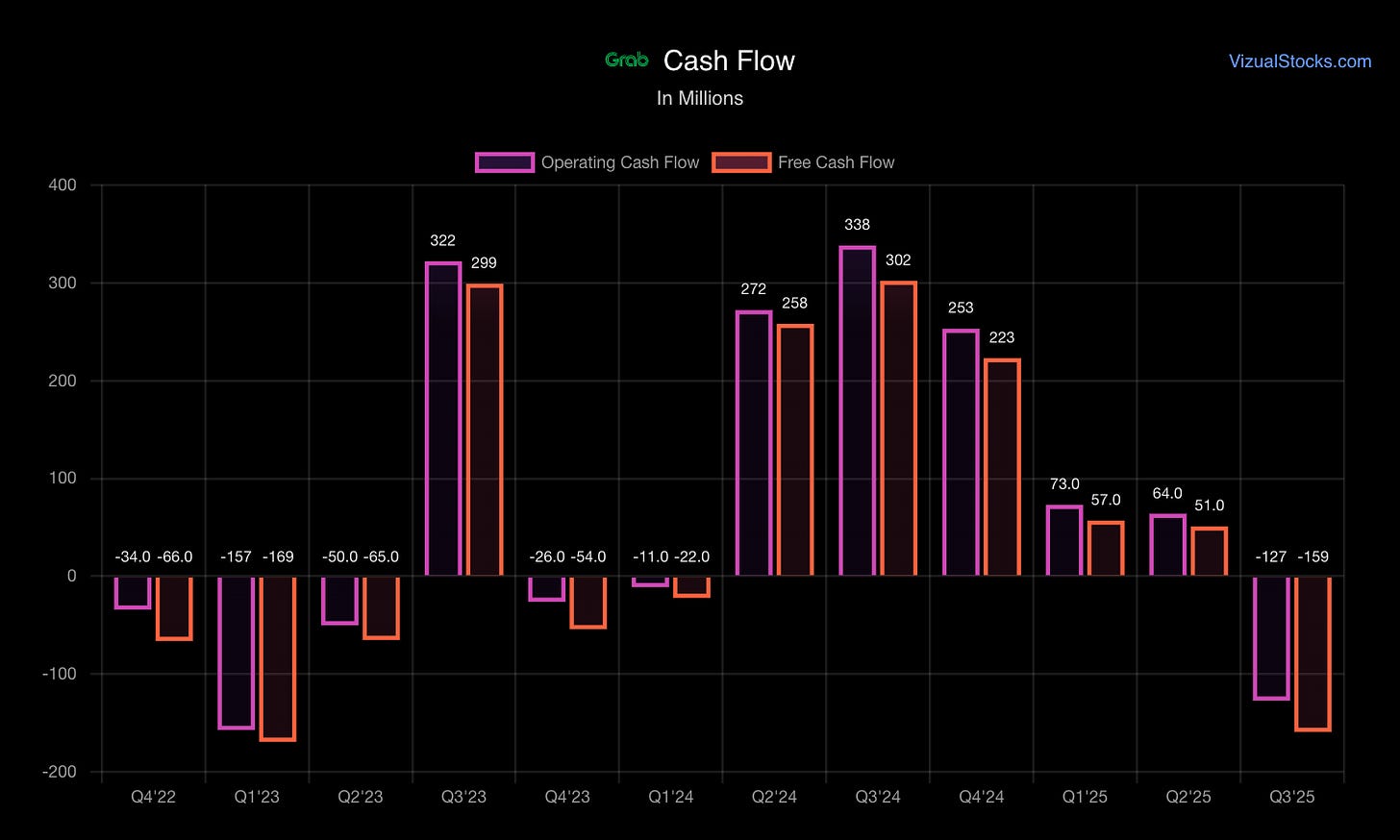
Working Capital: Negative working capital model (like Amazon)—consumers/merchants pay immediately, but GRAB settles with partners on delayed cycle = cash flow advantage.
Cash Conversion: Strong in mature Deliveries/Mobility. Digital banking drains cash in growth phase but promises future profitability once scale achieved.
Efficiency Assessment: Core business demonstrates excellent capital efficiency. Strategic bets (banking, AV) are appropriately capital-intensive but carry execution risk. Management’s “going concern” assessment suggests adequate liquidity runway.
Growth Drivers
Structural (Long-Term Tailwinds):
Southeast Asian Digital Adoption: 680M population, rising smartphone penetration, growing middle class, increasing trust in digital services
Financial Inclusion: 70%+ of SEA population underbanked; digital banking/lending addresses massive TAM
Urbanization: Migration to cities drives density economics for on-demand services
Regulatory Maturation: Gig economy frameworks being established (e.g., Singapore PWA 2024) create clearer operating environment
Company-Specific Levers:
Cross-Selling Within Ecosystem: GrabPay usage for rides/food → lending products → digital bank deposits (flywheel effect)
Frequency Increases: Average transactions per MTU expanding (25-30x annually, room to grow)
Autonomous Vehicles: Singapore robobus launch 2026 with WeRide/May Mobility; potential to reduce driver costs materially
Geographic Expansion: Deeper penetration in Vietnam, Philippines, Thailand; currently <20% market share in several markets
New Verticals: Insurance underwriting (launched Singapore 2024), grocery retail, logistics/fulfillment
Cyclical Factors:
Consumer discretionary spending sensitivity (food delivery, ride-hailing decline in downturns)
Fuel price volatility impacts driver supply
FX headwinds across SEA currencies vs. USD reporting
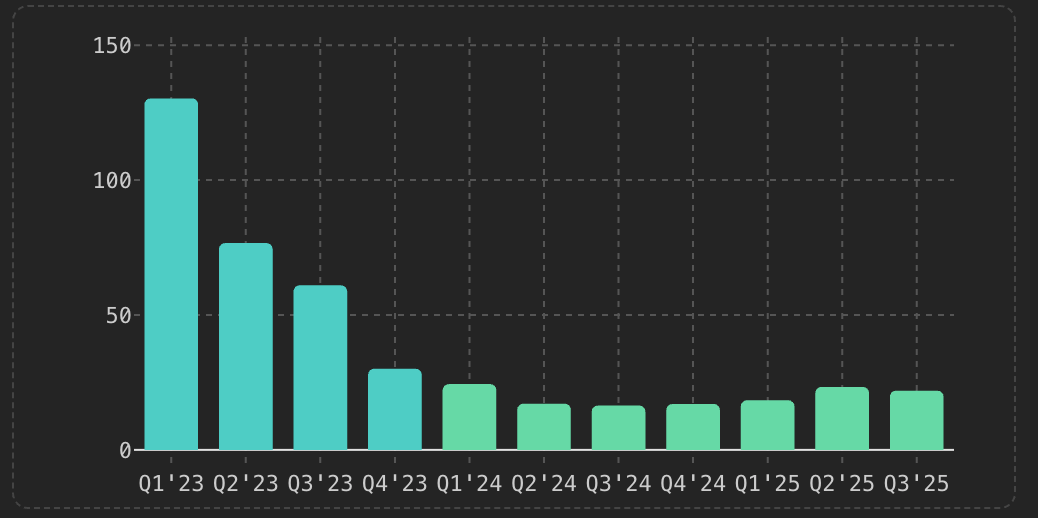
Chart: Revenue YoY Growth Moderating But StableGrowth Outlook: 18-25% revenue CAGR sustainable through 2027 driven by structural tailwinds. Risk: Regulatory clampdowns or competitive subsidization could compress growth.
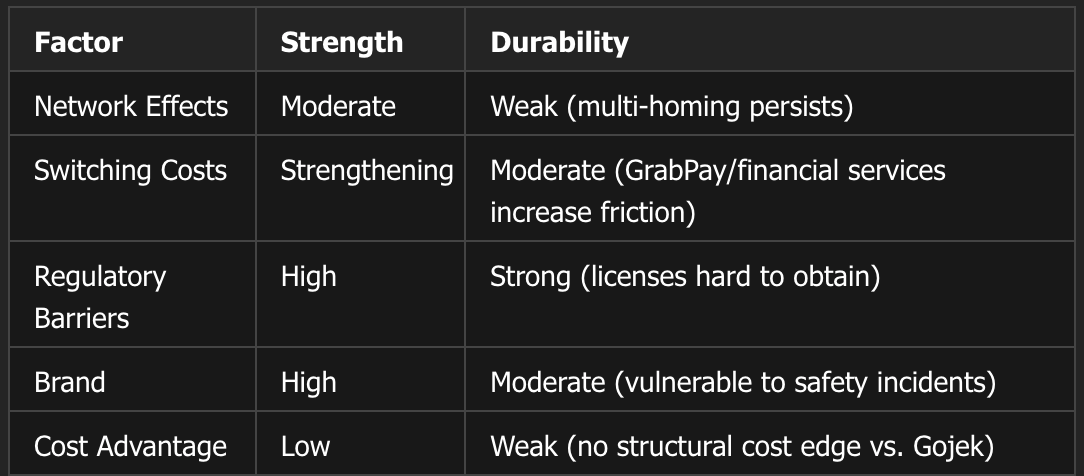
Competitive Edge (Moat Analysis)
Moat Type: Network Effects + Switching Costs (Moderate and Strengthening)
Two-Sided Network Effects
Mechanism: More consumers attract more drivers/merchants → better selection/availability attracts more consumers (virtuous cycle)
Evidence: 41.3M MTUs create liquidity advantage; driver-partners prioritize highest-volume platform
Limitation: Low barriers to multi-homing—drivers/merchants often use multiple platforms simultaneously
Ecosystem Lock-In (Switching Costs)
GrabPay Wallet: $X billion stored value creates friction to leave
Rewards Program: Points across services incentivize staying within ecosystem
Data Advantages: Personalization improves with usage (better recommendations, faster service)
Evidence: Cross-segment usage increasing; financial services penetration rising among existing users
Regional Scale Advantages
Regulatory Licenses: 100+ licenses across 8 countries = barrier to new entrants
Local Knowledge: Hyperlocal operations (800+ cities) difficult to replicate
Brand Recognition: “Grab” is verb in Singapore/Malaysia (like “Google” for search)
Strategic Partnerships
Uber non-compete (expires 1 year post-divestment; Uber holds equity stake)
Toyota (AV development, driver vehicle financing)
MUFG (financial services infrastructure)
Singtel (digital banking JV)
Moat Durability Assessment:
Financial Evidence of Moat:
Incentive ratio stabilizing at 10% (vs. 13.3% in 2022) = pricing power emerging
GAAP profitability achieved despite ongoing investments = economies of scale kicking in
Return metrics unavailable (fundamentals data issue), but positive EPS trajectory suggests improving ROIC
Competitive Threats:
Gojek (Indonesia, select SEA markets): Well-funded, similar superapp model. (Although it is to be noted that the Gojek threat is mostly limited to Indonesia, and for now, the company is going through several corporate governance issues, as cited in the media time to time.)
ShopeeFood/Foodpanda: E-commerce giants leveraging adjacent businesses
Single-Market Players: Xanh SM (Vietnam), Bolt/Robinhood (Thailand) with localized advantages
Uber Re-Entry Risk: Non-compete expires after Uber divests stake; familiarity with SEA markets = dangerous potential competitor
Verdict: Emerging moat is strengthening as the ecosystem deepens, but it is not yet wide. Financial services integration is a key differentiator versus single-vertical competitors. The next 3-5 years critical for moat widening.
Risk & Competitive Disadvantages
Regulatory Risk (HIGH)
Driver Classification:
Singapore PWA 2024 mandates platform operator registration, worker injury insurance, CPF contributions → increased costs
Malaysia, Thailand, Philippines, Indonesia developing similar frameworks
If reclassified as employees: wage/hour laws, benefits, unionization = structural margin compression
Foreign Ownership Restrictions:
Must remain “anchored in Singapore, controlled by Singaporeans” per MAS (Monetary Authority of Singapore) for digital banking license
Ownership structure constraints may limit strategic flexibility
Data Localization:
Multiple countries requiring local data storage = duplicative infrastructure costs
Data sharing restrictions limit cross-border synergies
Sector-Specific Regulations:
Vietnam: Mobility licenses required per province (hundreds of licenses) = operational complexity
Thailand: ETDA Law designates GRAB as “large digital service platform” → compliance officer, third-party audits, risk management frameworks
Philippines: VAT on digital services (12%) increases consumer costs
Competitive Risk (MODERATE to HIGH)
Intense Regional Rivalry:
Gojek (backed by Alibaba, Tencent) in Indonesia
Sea Limited’s ShopeeFood leveraging e-commerce base
Local champions with government favoritism (rise of nationalism)
Low Switching Costs:
Consumers/drivers easily multi-home across platforms
Price-sensitive markets → vulnerable to subsidization wars
Potential Uber Re-Entry:
Non-compete expires after stake divestment
Uber’s global scale + previous SEA operations = formidable threat
Execution Risk (MODERATE to HIGH)
Digital Banking:
Capital-intensive, regulatory-intensive
Competing against incumbents + new digital banks (Revolut, Wise expanding)
Credit risk as loan book scales
Still in “restricted operations” phase in Singapore (full license pending)
Autonomous Vehicles:
Technology unproven at scale; $60M Vay investment, WeRide/May Mobility partnerships = meaningful capital at risk
Regulatory approvals uncertain (currently testing in Punggol, Singapore)
Driver displacement concerns could trigger regulatory backlash
Financial Crimes / Compliance:
2020 anti-corruption investigation (voluntarily self-reported to DOJ) in one country
Operating in high-corruption jurisdictions increases exposure
Scams/fraud risks in digital banking (deepfakes, phishing increasing in SEA)
Business Model Risks (MODERATE to HIGH)
Incentive Dependency:
$1.8B incentives in FY2024 (10% of GMV)
Reducing incentives risks user/driver attrition
Competitive dynamics may prevent further optimization
Geographic Concentration:
Indonesia/Singapore ~60% of revenue
Adverse regulatory/economic event in major market = material impact
Macroeconomic Sensitivity:
Discretionary spending (food delivery, ride-hailing) declines in recessions
FX volatility across 8 currencies
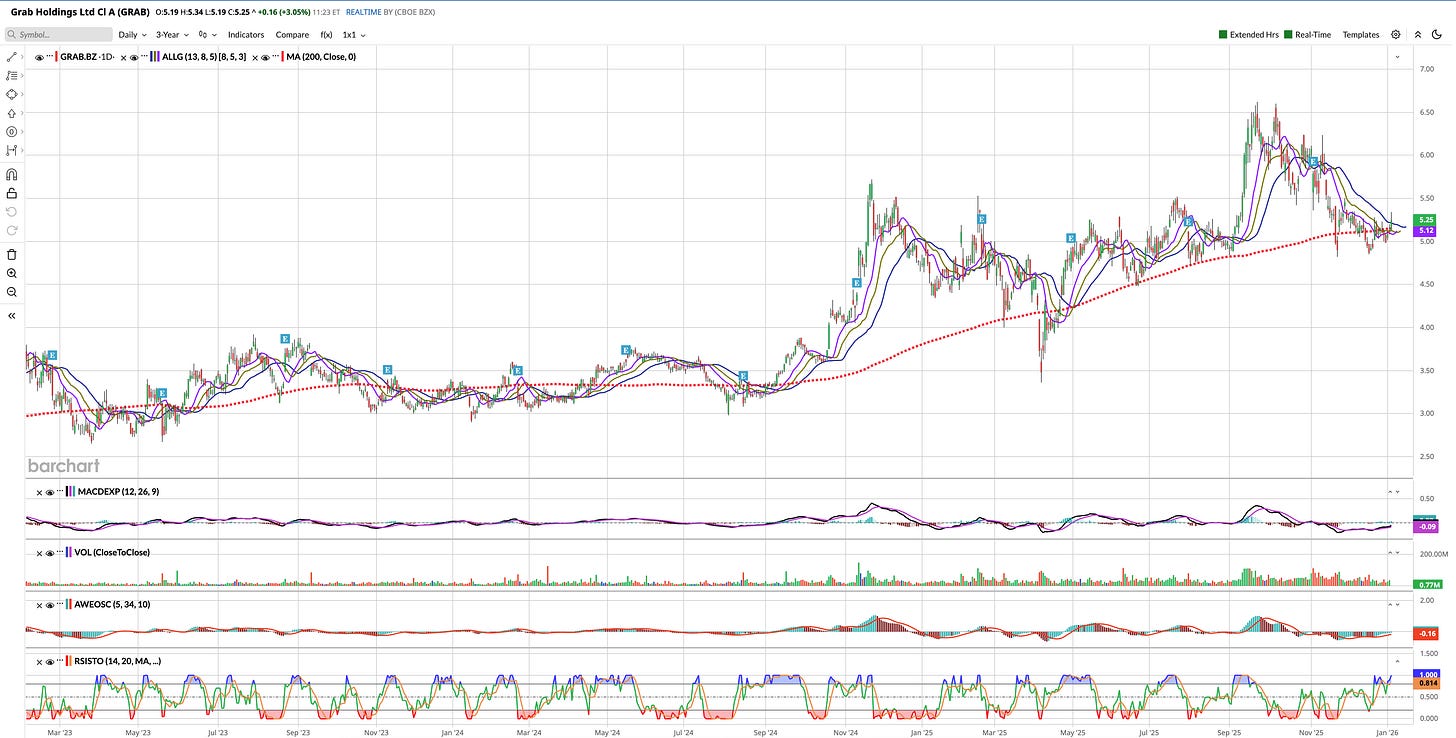
Basic Technical Analysis
Current Price: $5.25 (as of 06 Jan 2026)
52-Week Range: $3.995 - $6.62
Distance from 52W High: -20.7% (correction territory)
Distance from 52W Low: +31.4%
Chart: Price Trend: Consolidating After Q3 Earnings Drop (Source: Barchart.com)Current consolidation range: $4.80-$5.50
Major Moves Analysis
Bullish Runs:
Sep 12-18, 2025: $5.53 → $6.35 (+14.8%) on AV partnerships news, sector rotation into tech
Nov 10-13, 2025: $5.90 → $6.23 (+5.6%) on Vay investment announcement ($60M in remote driving tech)
Bearish Drops:
Nov 4-5, 2025: $6.07 → $5.64 (-7.1%) on Q3 earnings disappointment (missed EPS by 50%, revenue slight miss)
Nov 20-21, 2025: $5.31 → $4.90 (-7.7%) on GoTo merger concerns (Indonesia regulatory “golden share” proposal)
Oct 6-10, 2025: $6.39 → $5.86 (-8.3%) on broad tech sell-off, profit-taking after Sep rally
Indicator Analysis
Bullish Factors:
Volume Profile: Accumulation pattern near $5.00-$5.20 (higher volume on up days vs. down days in Jan’26)
Support Level: Strong buying interest at $4.80-$5.00 (tested Dec 19-23, held)
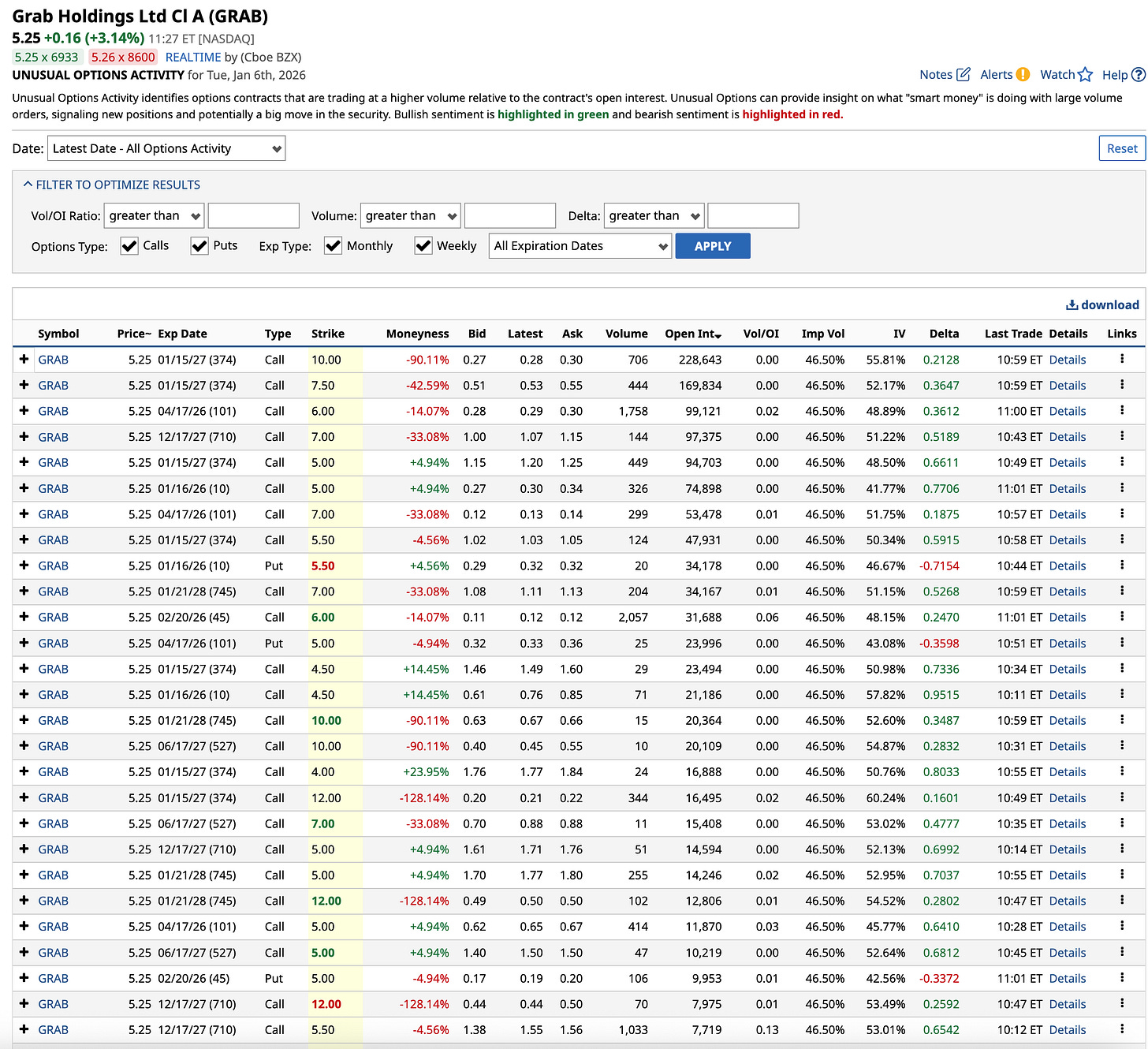
Options Flow: Bullish bias in Jan’26 — Multiple large call sweeps on Dec’27 $7 calls ($267K), Jan’28 $10 calls ($51K)
Analyst Upgrades: Barclays/Benchmark raised targets to $7 post-Q3
Bearish Factors:
Downtrend Since Nov 13: Lower highs ($6.23 → $5.54 → $5.46 → $5.25)
Below Key Moving Averages: Trading below 50-day, 100-day MA and just above 200-day MA
Q3 Earnings Reaction: Initial pop to $5.78 reversed sharply → lack of conviction
Put Activity: Jan’26 $5.50 puts saw aggressive accumulation ($500K+ in sweeps) suggesting downside hedging
Neutral/Mixed:
Relative Volume: Declining into year-end (typical seasonality)
Range-Bound: Consolidating in $4.80-$5.50 channel for 6+ weeks
Outlook
Base Case (60% probability): Consolidation continues in $4.80-$5.50 range through Q1’26 earnings (Feb 2026). Breakout requires either (a) Q4 earnings beat + guidance raise, or (b) major M&A/partnership announcement.
Bull Case (25% probability): Break above $5.60 on high volume → retest $6.00-$6.40 resistance zone. Catalysts: Digital banking full license approval, AV commercialization timeline, GoTo merger completion.
Bear Case (15% probability): Break below $4.80 → retest $4.40-$4.50 (May’25 lows). Risks: Regulatory clampdown, driver reclassification ruling, macro deterioration in SEA.
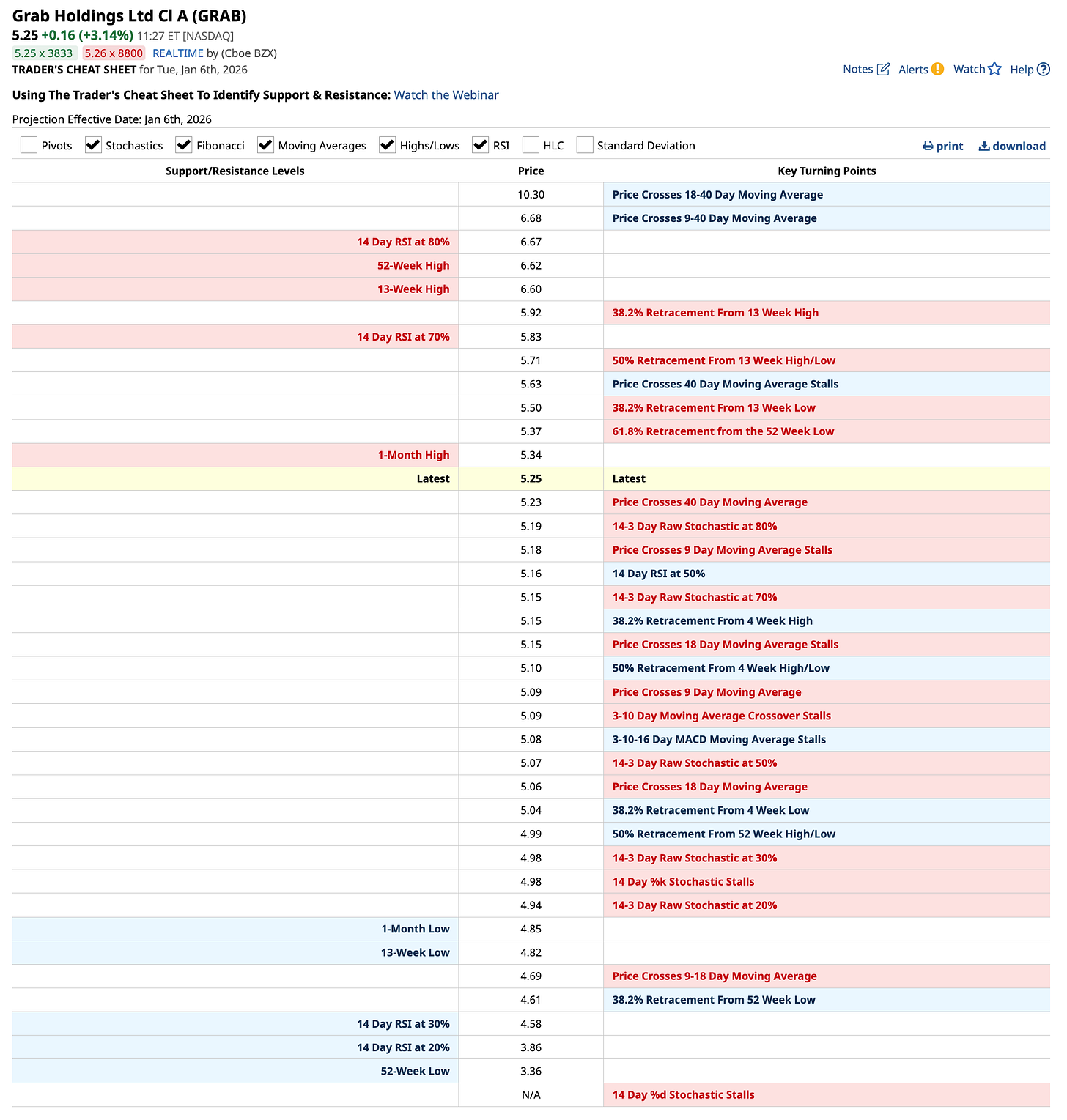
Key Levels to Watch:
Resistance: $5.60 (50-day MA), $6.00 (psychological), $6.40 (Oct high)
Support: $5.00 (Dec floor), $4.80 (critical), $4.40 (May’25 low)
Social Sentiment
GRAB maintains strong brand affinity across Southeast Asia but faces mixed sentiment online. Reddit/Twitter chatter in Q4’25 focused on three themes: (1) Optimism on AV partnerships (WeRide, May Mobility, Vay investments seen as forward-thinking), (2) Frustration over Q3 earnings miss (revenue growth decelerating to 22% raised concerns about market saturation), and (3) Debate over GoTo merger (Indonesia’s “golden share” proposal viewed as regulatory overhang).
StockTwits data shows GRAB among “top watched” tickers in emerging markets category, indicating retail interest. Fintwit sentiment leans cautiously bullish—recognition of structural growth story offset by near-term execution concerns. Local SEA forums (HardwareZone Singapore, Kaskus Indonesia) reveal consumer satisfaction with service quality but complaints about rising prices and reduced driver incentives.
Analyst community (per recent CNBC/Bloomberg coverage) views GRAB as “best-in-class” SEA internet play but emphasizes need for sustained profitability proof. Digital banking progress is closely watched—failure to obtain full Singapore license by mid-2026 would be viewed negatively.
Overall Sentiment Grade: B (Moderately Positive) — Strong fundamentals story, but recent stumbles and competitive/regulatory headwinds create cautious tone.
Investment Thesis Summary
Bull Case:
Structural growth in underpenetrated SEA digital services market (680M population TAM)
Superapp ecosystem creating switching costs and cross-sell opportunities
Path to sustained profitability demonstrated (positive EPS 7 of last 8 quarters)
Strategic bets (digital banking, AV) offer significant upside if executed
33% upside to consensus PT; trading near support after Q3 selloff = favorable entry
Bear Case:
Regulatory risk across 8 jurisdictions could materially increase costs or restrict operations
Competitive intensity remains high; moat not yet proven durable
Digital banking capital drag continues; ROI uncertain
Geographic concentration + macro sensitivity = earnings volatility
Uber re-entry risk if non-compete expires
Verdict for Long-Term Investors:
GRAB represents a “buy on dips” opportunity for patient capital. The company is executing on the transition from growth-at-any-cost to profitable growth, but faces legitimate execution and regulatory risks. The structural tailwind of Southeast Asian digitalization provides multi-year runway, and recent price weakness ($5.25 vs. $6.62 high) offers improved risk/reward. However, this is not a set-it-and-forget-it holding—active monitoring of regulatory developments and digital banking milestones is essential.
Recommended Position Sizing: 2-4% of growth-oriented portfolio (moderate-high risk tolerance). Consider scaling in near $5.00 support if further weakness materializes.
Additional Charts
Image illustrating Unusal Options sorted with O/I (Source: Barchat.com)
Source: Barchat.com
Source: VizualStocks.com
Source: VizualStocks.com
Source: VizualStocks.com
Source: VizualStocks.com
Source: VizualStocks.com
Source: VizualStocks.com
Source: VizualStocks.com
Source: VizualStocks.com
Disclaimer
This article is provided for educational, informational, and entertainment purposes only. It does not constitute financial advice, investment advice, trading advice, or any other form of professional advice.
The views and opinions expressed are solely those of the author and are based on personal interpretation, experience, and publicly available information at the time of writing. They should not be relied upon as a basis for making financial, investment, or trading decisions.
All investments carry risk, including the possible loss of capital. Past performance is not indicative of future results. You are solely responsible for your own financial decisions.
Before making any investment or financial decision, you should conduct your own independent research and due diligence, and consult with a qualified financial advisor, accountant, or other licensed professional where appropriate.
The author accepts no responsibility or liability for any losses, damages, or outcomes arising directly or indirectly from the use of, reliance on, or interpretation of the information contained in this article.



Great read over my lunch break!
Refreshing to see such a sensible outlook (on the base, bear and bull cases). I’m hoping to see GRAB utilise the capital they’re sitting on for more acquisitions.
I’d be happy with a >$6.00 come 2027.
Hope to see you on Amits stream again sometime soon!